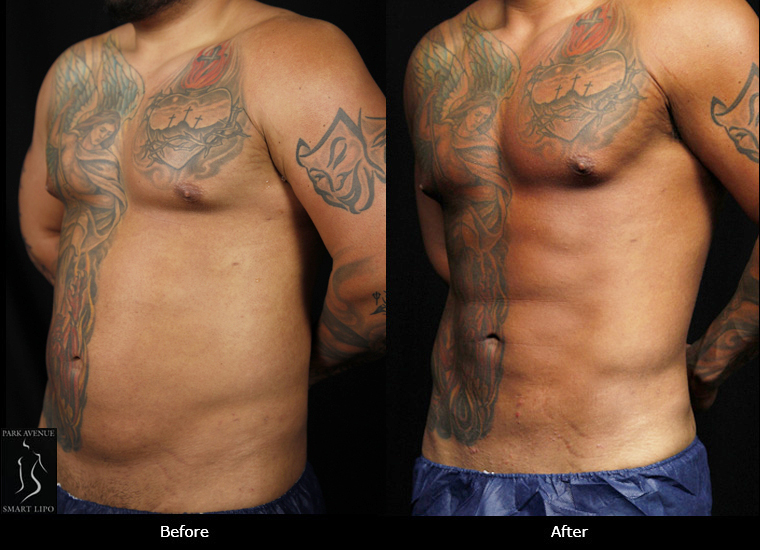
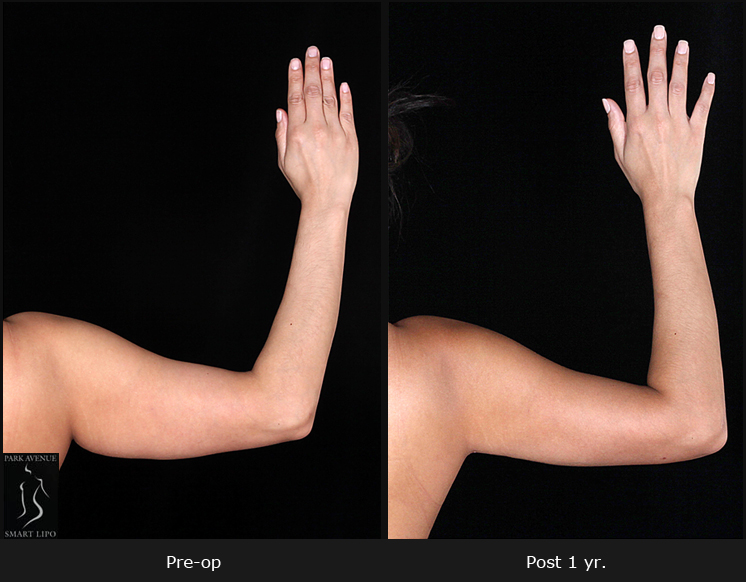
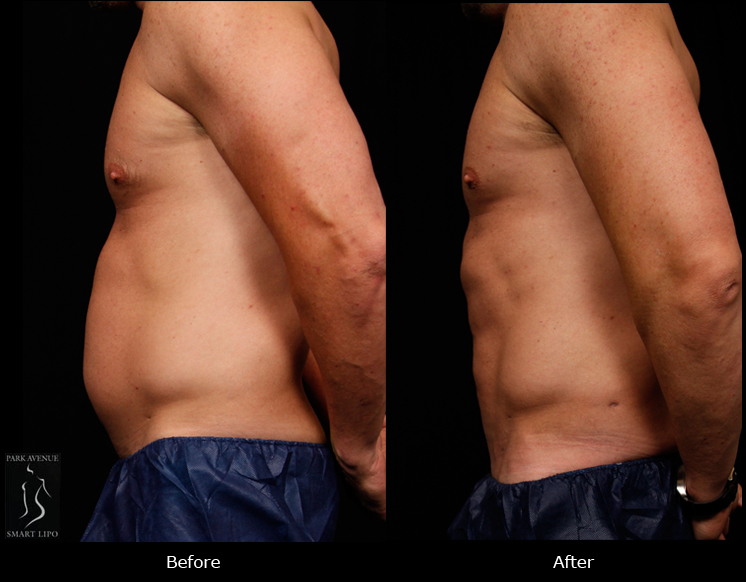
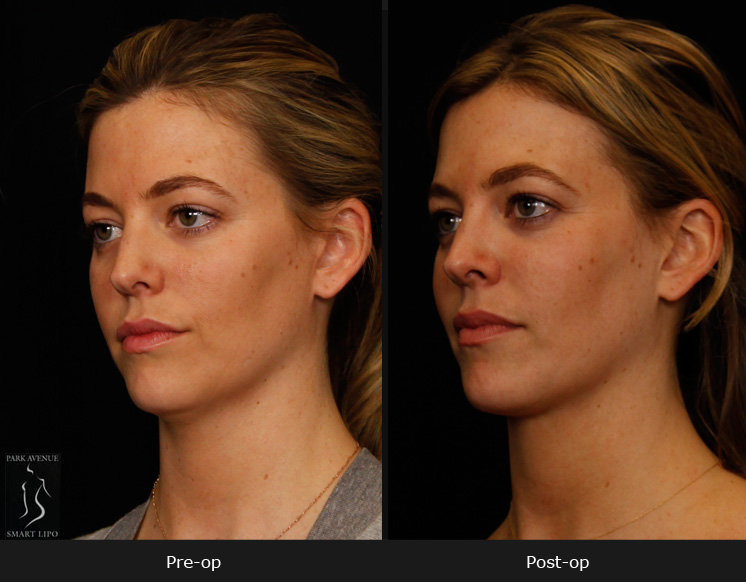
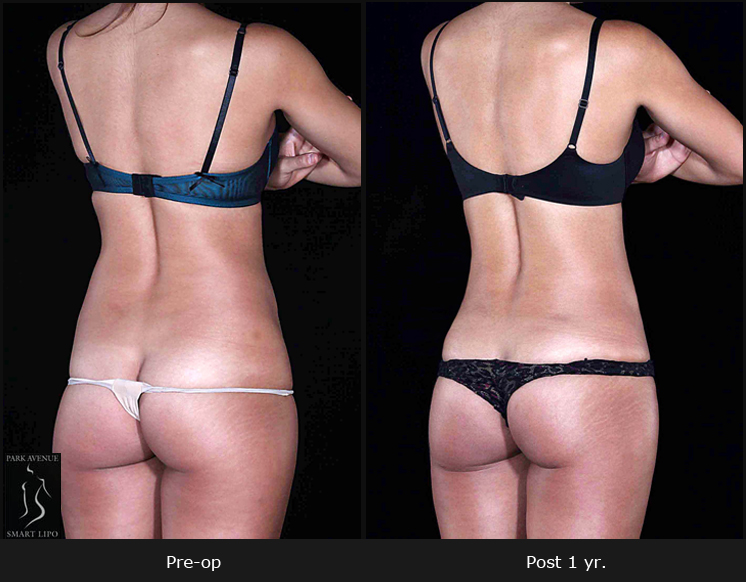
In NYC, liposuction is one of the most commonly performed procedures. It is widely accepted due to its ability to address aesthetic concerns by removing stubborn fat deposits that are resistant to traditional weight loss measures. In addition to addressing aesthetic concerns, liposuction is reportedly easing certain medical issues. According to a recent case report in the New England Journal of Medicine, the procedure can also reduce the pain and swelling associated with lymphedema.
Lymphedema is the swelling that occurs when lymph fluid cannot flow normally and builds up in the soft tissues of a limb. It usually occurs in parts of the body where lymph nodes have been removed or damaged frequently by cancer treatment and parasitic infections. According to the case report, liposuction for primary or secondary lymphedema eased the associated limb swelling and pain. Liposuction also showed good results in lowering the volume of fluid in a limb with severe lymphedema related to breast cancer treatment.
In the study, three patients affected by lymphedema underwent liposuction to remove subcutaneous adipose tissue from the swelling limb. Surgeons removed 1,200 and 1,900 mL of tissue from two patients with lymphedema secondary to treatment for breast cancer. A third patient with primary lymphedema affecting a leg had 2,800 mL of tissue removed. The patients who had liposuction only had the procedure on an affected limb. The two patients who had liposuction on arms also saw improvement in their hand. The patient who had liposuction on her leg saw improvement in the lymphedema affecting her foot.
The study author wrote, “Our results show that liposuction … may have a physiological benefit…”
He noted that liposuction improves lymphatic flow and increases quality of life. It actually helps underlying lymphatic system to move the fluid. However, he cautioned that patients would still have to take conservative measures, such as wearing compression garments to promote fluid drainage.
Several theories are offered to describe why liposuction was more effective than expected, though none have been proven. One theory is that fat removal eases pressure on the remaining lymph nodes and vessels, allowing them to function better. Another theory is that the fat may produce fluid, and therefore removing it, might reduce overall fluid.